What is Petrol engine and who invented petrol engine?
The Otto Engine is also known as Petrol Engine or Internal combustion engine. In this engine working substance is air. The Otto Engine has a cylinder fitted with a frictionless piston. The cylinder has two walves. One walve consider as I is known as Inlet. The other walve is consider as O is known as Outlet. Through the Inlet walve petrol air vapour is admitted The cylinder. Through the outlet walve the burnt out gases are pushed out. Both I and O are operated by the movement of the piston. Otto engine changed into a massive desk bound single-cylinder inner combustion 4-stroke engine designed by means of the German Nicolaus Otto. It became a low-RPM machine, and best fired each different stroke because of the Otto cycle, also designed with the aid of Otto.
Working of Otto Engine
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft . A stroke refers to the full tour of the piston alongside the cylinder, in either direction. The four separate strokes are termed as
- Intake
- Compression
- Combustion
- Exhaust
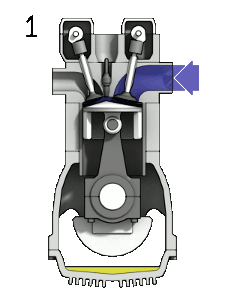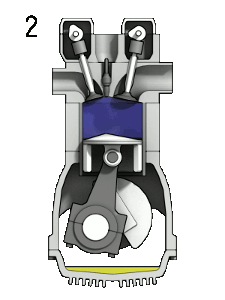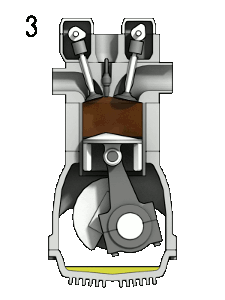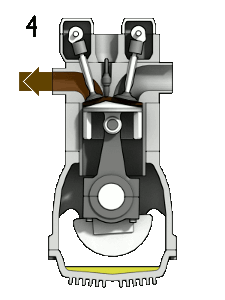
1.Intake: Also known as induction or suction. This stroke of the piston begins at top dead center (T.D.C.) and ends at bottom dead center (B.D.C.). On this stroke the intake valve should be in the open position even as the piston pulls an air-gas combination into the cylinder via producing vacuum stress into the cylinder thru its downward.The piston is transferring down as air is being sucked in by using the downward motion towards the piston.
2.Compression: This stroke begins at B.D.C, or just at the end of the suction stroke, and ends at T.D.C. On this stroke the piston compresses the air-gas mixture in coaching for ignition for the duration of the electricity stroke (below). each the consumption and exhaust valves are closed all through this level.
3.Combustion: Also known as power or ignition. This is the start of the second one revolution of the 4 stroke cycle. At this factor the crankshaft has completed a full 360 degree revolution. While the piston is at T.D.C. (the give up of the compression stroke) the compressed air-fuel aggregate is ignited via a spark plug (in a gas engine) or by heat generated by means of excessive compression (diesel engines), forcefully returning the piston to B.D.C. This stroke produces mechanical paintings(work) from the engine to turn the crankshaft.
4.Exhaust: Also known as outlet. During the exhaust stroke, the piston, once again, returns from B.D.C. to T.D.C. while the exhaust valve is open. This movement expels the spent air-gasoline combination via the exhaust valve.
Graphics Interchange Format
For the understanding purpose Graphic Interchange Format (GIF) image is displayed above it explains the the working of Otto Engine
Question of the day - Comment below:
Who is the father of Physics?



Sir Issac Newton
ReplyDeleteCongrats! correct answer
DeleteThis comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
DeleteEither Einstein or Newton??
ReplyDeleteNewton is the correct answer
DeleteNewton?
ReplyDeleteYeah you're closer
Delete