What are Electromagnetic Waves?
Electromagnetic waves are also referred to as EM waves. EM waves are waves that are created due to vibrations between an electric field and a magnetic field. In different phrases, EM waves are composed of oscillating magnetic and electric fields.Electromagnetic waves are formed when an electric field comes in contact with a magnetic field. They are hence known as ‘electromagnetic’ waves. The electric field and magnetic field of an EM waves are normal to each other.
Property of Electromagnetic waves
- Electromagnetic waves are propagated by oscillating electric and magnetic field oscillation at right angles to each other.
- They are transverse in nature.
- They are not reflected by electric and magnetic fields.
- They travel at the speed of 3 x 10⁸ ms-¹ at the vaccum.
Applications of Electromagnetic Waves
- Electromagnetic radiations can transmit energy in vacuum or using no medium at all.
- EM waves play an vital function in conversation generation.
- Electromagnetic waves are used in RADARS.
- UV rays are used to stumble on forged financial institution notes. Actual financial institution notes don’t flip fluorescent beneath the UV mild.
- IR is used for night vision and is used in security camera.
Graphical Representation of Electromagnetic Waves
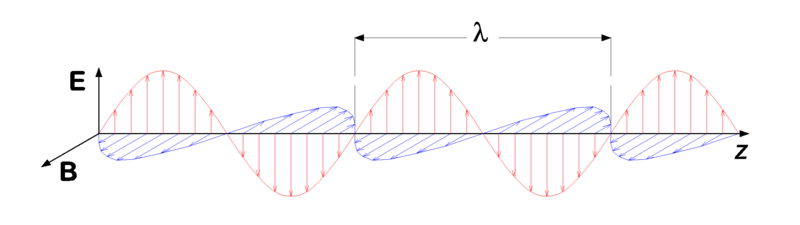 |
| Image source:Wikimedia |
| Electromagnetic waves are shown by a sinusoidal graph. It consists of time-various electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each different and are also perpendicular to the path of propagation of waves. Electromagnetic waves are transverse in nature. the best point of the wave is known as crest while the lowest point is referred to as a trough. In vacuum, the waves journey at a constant pace of 3 x 10^8 m.s-1 |
How are Electromagnetic waves formed?
Normally , anelectric area is producedby way of a charged particle. Apressure is exertedthrough thiselectric powered subject onother chargedparticles .high-quality charges boost up in the path ofthe field andpoor prices boost up in aroute opposite to thedirection ofthe field .
- The Magnetic
area is producedby means of ashifting charged particle. Aforce is exertedwith the aid of this magneticarea onother moving debris . Theforce onthose charges isusually perpendicular to theroute in their velocity andconsequently most effective adjustments thecourse ofthe speed ,not the speed .
- So, the electromagnetic
subject is producedby means of an accelerating charged particle. Electromagnetic waves arenot anything however electric powered and magnetic fieldstravelling thru loose space withthe speed oflight c. An accelerating charged particle iswhilst the charged particle oscillatesapproximately an equilibriumrole . If the frequency of oscillation of the charged particle is f, then it produces an electromagnetic wave with frequency f. The wavelength λ of this wave is givenby λ = c/f. Electromagnetic wavestransfer electricity via area.
Tags:

